 SpringSecurity
SpringSecurity
SpringSecurity
一、介绍
1、SpringSecurity
认证功能几乎是每个项目都要具备的功能,并且它与业务无关,市面上有很多认证框架,如:Apache Shiro、CAS、Spring Security等。Spring Security是spring家族的一份子且和Spring Cloud集成的很好。Spring Security 是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架,它是一个专注于为 Java 应用程序提供身份验证和授权的框架。
Spring Security是Spring项目组提供的安全服务框架,核心功能包 括认证和授权。它为系统提供了声明式安全访问控制功能,减少了 为系统安全而编写大量重复代码的工作。
介绍
- 认证
认证即系统判断用户的身份是否合法,合法可继续访问,不合法则拒绝访问。
常见的用户身份认证方式有:用户名密码登录、二维码登录、手机短信登录、脸部识别认证、指纹认证等方式。 认证是为了保护系统的隐私数据与资源,用户的身份合法才能访问 该系统的资源。
- 授权
授权即认证通过后,根据用户的权限来控制用户访问资源的过程, 拥有资源的访问权限则正常访问,没有权限则拒绝访问。 比如在一 些视频网站中,普通用户登录后只有观看免费视频的权限,而VIP用户登录后,网站会给该用户提供观看VIP视频的权限。
认证是为了保证用户身份的合法性,授权则是为了更细粒度的对隐私数据进行划分,控制不同的用户能够访问不同的资源。
举个例子:认证是公司大门识别你作为员工能进入公司,而授权则 是由于你作为公司会计可以进入财务室,查看账目,处理财务数据。
2、OAuth2
像微信扫码认证这种第三方认证的方式一般都是基于OAuth2协议实现,OAUTH协议为用户资源的授权提供了一个安全的、开放而又简易的标准。同时,任何第三方都可以使用OAUTH认证服务,任何服务提供商都可以实现自身的OAUTH认证服务,因而OAUTH是开放的。
业界提供了OAUTH的多种实现如PHP、JavaScript,Java,Ruby等各种语言开发包,大大节约了程序员的时间,因而OAUTH是简易的。互联网很多服务如Open API,很多大公司如Google,Yahoo,Microsoft等都提供了OAUTH认证服务,这些都足以说明OAUTH标准逐渐成为开放资源授权的标准。
Oauth协议目前发展到2.0版本,1.0版本过于复杂,2.0版本已得到广泛应用。
Oauth2.0的认证流程,如下:
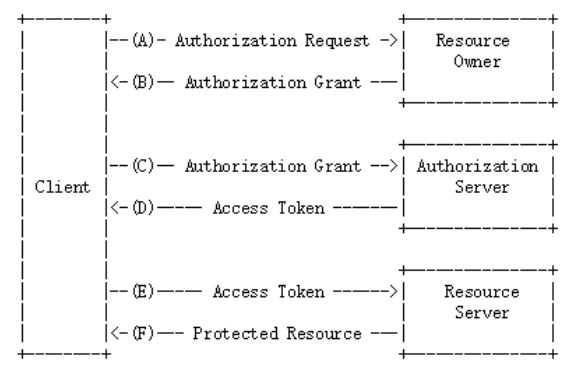
Oauth2包括以下角色:
1、客户端
- 本身不存储资源,需要通过资源拥有者的授权去请求资源服务器的资源,比如:手机客户端、浏览器等。
2、资源拥有者
通常为用户,也可以是应用程序,即该资源的拥有者。
A表示 客户端请求资源拥有者授权。
B表示 资源拥有者授权客户端访问自己的用户信息。
3、授权服务器(也称认证服务器)
认证服务器对资源拥有者进行认证,还会对客户端进行认证并颁发令牌。
C 客户端携带授权码请求认证。
D认证通过颁发令牌。
4、资源服务器
存储资源的服务器。
E表示客户端携带令牌请求资源服务器获取资源。
F表示资源服务器校验令牌通过后提供受保护资源。
二、快速入门
1、引入依赖
向pom.xml加入Spring Security所需要的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、进行安全配置
WebSecurityConfig.java
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//配置用户信息服务
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
//这里配置用户信息,这里暂时使用这种方式将用户存储在内存中
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("zhangsan").password("123").authorities("p1").build());
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("lisi").password("456").authorities("p2").build());
return manager;
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
//密码为明文方式
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
//配置安全拦截机制
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/r/**").authenticated()//访问/r开始的请求需要认证通过
.anyRequest().permitAll()//其它请求全部放行
.and()
.formLogin().successForwardUrl("/login-success");//登录成功跳转到/login-success
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout");//退出地址
}
}
主要配置三部分内容:
1、用户信息
在内存配置两个用户:zhangsan、lisi。zhangsan用户拥有的权限为p1,lisi用户拥有的权限为p2
2、密码方式
暂时采用明文方式
3、安全拦截机制
/r/**开头的请求需要认证,登录成功到成功页面
3、测试
之后可以编写介个接口分别进行测试,下边在controller中配置/r/r1需要p1权限,/r/r2需要p2权限。
hasAuthority('p1')表示拥有p1权限方可访问。
@RestController
public class LoginController {
....
@RequestMapping("/r/r1")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('p1')")//拥有p1权限方可访问
public String r1(){
return "访问r1资源";
}
@RequestMapping("/r/r2")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('p2')")//拥有p2权限方可访问
public String r2(){
return "访问r2资源";
}
...
三、工作原理
通过测试认证和授权两个功能,我们了解了Spring Security的基本使用方法,下边了解它的工作流程。
Spring Security所解决的问题就是安全访问控制,而安全访问控制功能其实就是对所有进入系统的请求进行拦截,校验每个请求是否能够访问它所期望的资源。根据前边知识的学习,可以通过Filter或AOP等技术来实现,Spring Security对Web资源的保护是靠Filter实现的,所以从这个Filter来入手,逐步深入Spring Security原理。
当初始化Spring Security时,会创建一个名为SpringSecurityFilterChain的Servlet过滤器,类型为org.springframework.security.web.FilterChainProxy,它实现了javax.servlet.Filter,因此外部的请求会经过此类,下图是Spring Security过虑器链结构图:
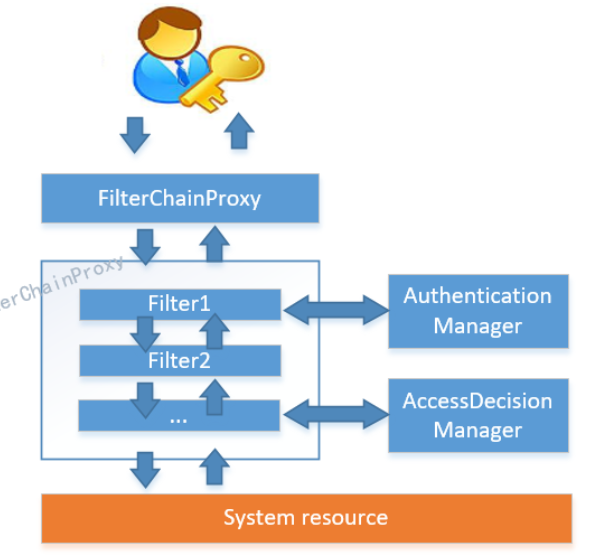
FilterChainProxy是一个代理,真正起作用的是FilterChainProxy中SecurityFilterChain所包含的各个Filter,同时这些Filter作为Bean被Spring管理,它们是Spring Security核心,各有各的职责,但他们并不直接处理用户的认证,也不直接处理用户的授权,而是把它们交给了 认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)和决策管理器(AccessDecisionManager) 进行处理。
spring Security功能的实现主要是由一系列过滤器链相互配合完成。
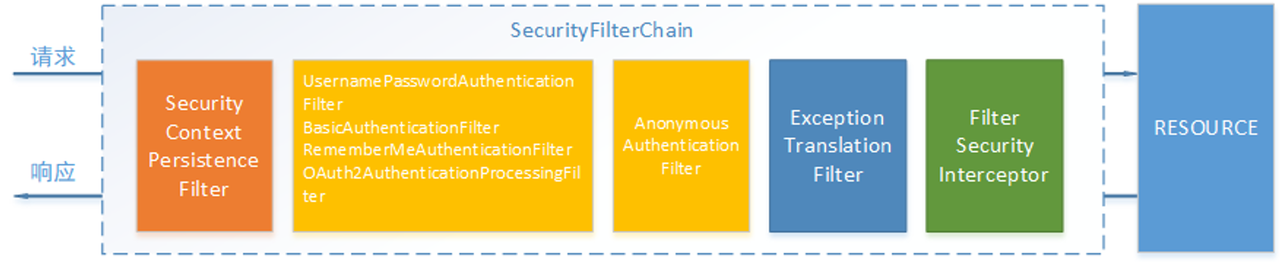
下面介绍过滤器链中主要的几个过滤器及其作用:
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 这个Filter是整个拦截过程的入口和出口(也就是第一个和最后一个拦截器),会在请求开始时从配置好的
SecurityContextRepository中获取SecurityContext,然后把它设置给SecurityContextHolder。在请求完成后将SecurityContextHolder持有的SecurityContext再保存到配置好的SecurityContextRepository,同时清除securityContextHolder所持有的SecurityContext;UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 用于处理来自表单提交的认证。该表单必须提供对应的用户名和密码,其内部还有登录成功或失败后进行处理的
AuthenticationSuccessHandler和AuthenticationFailureHandler,这些都可以根据需求做相关改变;FilterSecurityInterceptor 是用于保护web资源的,使用
AccessDecisionManager对当前用户进行授权访问,前面已经详细介绍过了;ExceptionTranslationFilter 能够捕获来自 FilterChain 所有的异常,并进行处理。但是它只会处理两类异常:
AuthenticationException和AccessDeniedException,其它的异常它会继续抛出。
Spring Security的执行流程如下:
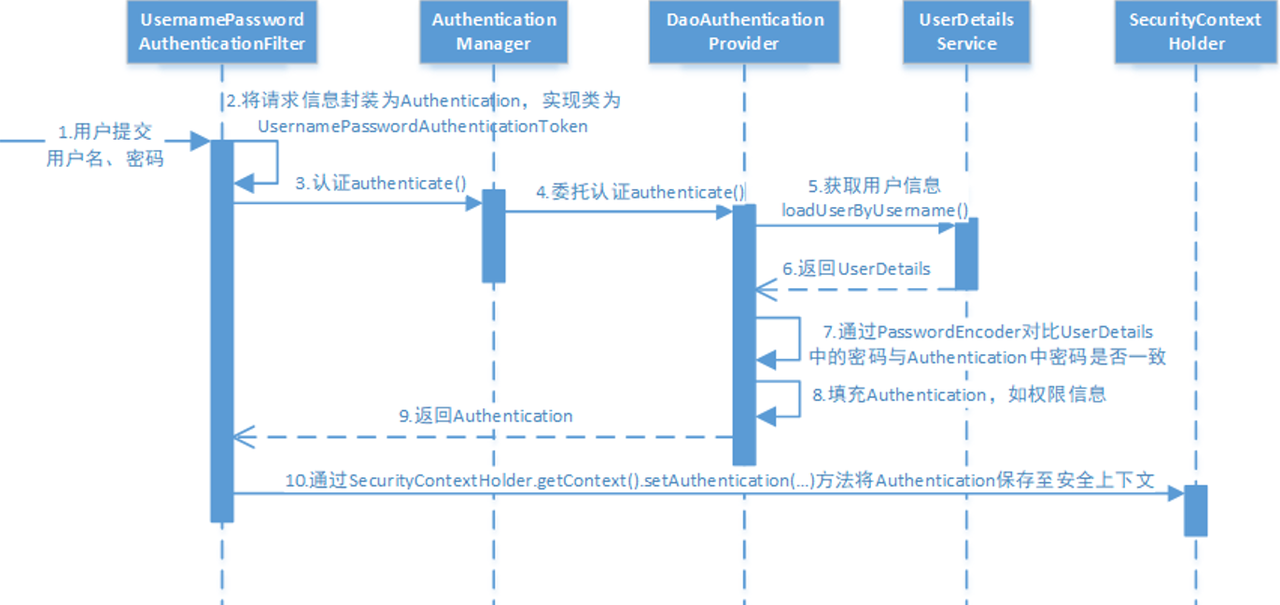
- 用户提交用户名、密码被
SecurityFilterChain中的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器获取到,封装为请求Authentication,通常情况下是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken这个实现类。
- 用户提交用户名、密码被
- 然后过滤器将
Authentication提交至认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)进行认证
- 然后过滤器将
- 认证成功后,
AuthenticationManager身份管理器返回一个被填充满了信息的(包括上面提到的权限信息,身份信息,细节信息,但密码通常会被移除)Authentication实例。
- 认证成功后,
SecurityContextHolder安全上下文容器将第3步填充了信息的Authentication,通过SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(…)方法,设置到其中。
可以看出AuthenticationManager接口(认证管理器)是认证相关的核心接口,也是发起认证的出发点,它的实现类为ProviderManager。而Spring Security支持多种认证方式,因此ProviderManager维护着一个List<AuthenticationProvider>列表,存放多种认证方式,最终实际的认证工作是由AuthenticationProvider完成的。咱们知道web表单的对应的AuthenticationProvider实现类为DaoAuthenticationProvider,它的内部又维护着一个UserDetailsService负责UserDetails的获取。最终AuthenticationProvider将UserDetails填充至Authentication。
四、OAuth2使用
1、OAuth2在学成在线项目中的应用
Oauth2是一个标准的开放的授权协议,应用程序可以根据自己的要求去使用Oauth2,本项目使用Oauth2实现如下目标:
1、学成在线访问第三方系统的资源。
本项目要接入微信扫码登录所以本项目要使用OAuth2协议访问微信中的用户信息。
2、外部系统访问学成在线的资源 。
同样当第三方系统想要访问学成在线网站的资源也可以基于OAuth2协议。
3、学成在线前端(客户端) 访问学成在线微服务的资源。
本项目是前后端分离架构,前端访问微服务资源也可以基于OAuth2协议进行认证。
2、OAuth2的授权模式
Spring Security支持OAuth2认证,OAuth2提供授权码模式、密码模式、简化模式、客户端模式等四种授权模式,前边举的微信扫码登录的例子就是基于授权码模式,这四种模式中授权码模式和密码模式应用较多。
1)授权码模式
OAuth2的几个授权模式是根据不同的应用场景以不同的方式去获取令牌,最终目的是要获取认证服务颁发的令牌,最终通过令牌去获取资源。
授权码模式简单理解是使用授权码去获取令牌,要想获取令牌先要获取授权码,授权码的获取需要资源拥有者亲自授权同意才可以获取。
下图是授权码模式的交互图:

以黑马网站微信扫码登录为例进行说明:
1、用户打开浏览器。
2、通过浏览器访问客户端即黑马网站。
3、用户通过浏览器向认证服务请求授权,请求授权时会携带客户端的URL,此URL为下发授权码的重定向地址。
4、认证服务向资源拥有者返回授权页面。
5、资源拥有者亲自授权同意。
6、通过浏览器向认证服务发送授权同意。
7、认证服务向客户端地址重定向并携带授权码。
8、客户端即黑马网站收到授权码。
9、客户端携带授权码向认证服务申请令牌。
10、认证服务向客户端颁发令牌。
授权码模式测试
首先要配置授权服务器即上图中的认证服务器,需要配置授权服务及令牌策略。
配置AuthorizationServer:
1)ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer:用来配置客户端详情服务(ClientDetailsService),
随便一个客户端都可以随便接入到它的认证服务吗?答案是否定的,服务提供商会给批准接入的客户端一个身份,用于接入时的凭据,有客户端标识和客户端秘钥,在这里配置批准接入的客户端的详细信息。
2)AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer:用来配置令牌(token)的访问端点和令牌服务(token services)。
3)AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer:用来配置令牌端点的安全约束.
package com.xuecheng.auth.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.configurers.ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableAuthorizationServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.AuthorizationServerTokenServices;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Resource(name="authorizationServerTokenServicesCustom")
private AuthorizationServerTokenServices authorizationServerTokenServices;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
//客户端详情服务
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients)
throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()// 使用in-memory存储
.withClient("XcWebApp")// client_id
// .secret("XcWebApp")//客户端密钥
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("XcWebApp"))//客户端密钥
.resourceIds("xuecheng-plus")//资源列表
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code", "password","client_credentials","implicit","refresh_token")// 该client允许的授权类型authorization_code,password,refresh_token,implicit,client_credentials
.scopes("all")// 允许的授权范围
.autoApprove(false)//false跳转到授权页面
//客户端接收授权码的重定向地址
.redirectUris("http://www.51xuecheng.cn")
;
}
//令牌端点的访问配置
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints
.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)//认证管理器
.tokenServices(authorizationServerTokenServices)//令牌管理服务
.allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.POST);
}
//令牌端点的安全配置
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security){
security
.tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()") //oauth/token_key是公开
.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()") //oauth/check_token公开
.allowFormAuthenticationForClients() //表单认证(申请令牌)
;
}
}
配置TokenConfig.java令牌策略配置类:
暂时先使用InMemoryTokenStore在内存存储令牌,令牌的有效期等信息配置如下:
package com.xuecheng.auth.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.AuthorizationServerTokenServices;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.DefaultTokenServices;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.TokenEnhancerChain;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.TokenStore;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.store.JwtAccessTokenConverter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.store.JwtTokenStore;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
**/
@Configuration
public class TokenConfig {
private String SIGNING_KEY = "mq123";
@Autowired
@Lazy
TokenStore tokenStore;
// @Bean
// public TokenStore tokenStore() {
// //使用内存存储令牌(普通令牌)
// return new InMemoryTokenStore();
// }
@Autowired
@Lazy
private JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter;
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(accessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey(SIGNING_KEY);
return converter;
}
//令牌管理服务
@Bean(name="authorizationServerTokenServicesCustom")
public AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenService() {
DefaultTokenServices service=new DefaultTokenServices();
service.setSupportRefreshToken(true);//支持刷新令牌
service.setTokenStore(tokenStore);//令牌存储策略
TokenEnhancerChain tokenEnhancerChain = new TokenEnhancerChain();
tokenEnhancerChain.setTokenEnhancers(Arrays.asList(accessTokenConverter));
service.setTokenEnhancer(tokenEnhancerChain);
service.setAccessTokenValiditySeconds(7200); // 令牌默认有效期2小时
service.setRefreshTokenValiditySeconds(259200); // 刷新令牌默认有效期3天
return service;
}
}
配置认证管理Bean
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
....
重启认证服务
- 1)get请求获取授权码
地址:
http://localhost:63070/auth/oauth/authorize?client_id=XcWebApp&response_type=code&scope=all&redirect_uri=http://www.51xuecheng.cn
参数列表如下:
- client_id:客户端准入标识。
- response_type:授权码模式固定为code。
- scope:客户端权限。
- redirect_uri:跳转uri,当授权码申请成功后会跳转到此地址,并在后边带上code参数(授权码)。
输入账号zhangsan、密码123登录成功,输入:
/oauth/authorize?client_id=XcWebApp&response_type=code&scope=all&redirect_uri=http://www.51xuecheng.cn
显示授权页面:授权“XcWebApp”访问自己的受保护资源?选择同意。
2)请求成功
重定向至
http://www.51xuecheng.cn/?code=授权码,比如:http://www.51xuecheng.cn/?code=Wqjb5H3)使用httpclient工具post申请令牌
/auth/oauth/token?client_id=XcWebApp&client_secret=XcWebApp&grant_type=authorization_code&code=授权码&redirect_uri=http://www.51xuecheng.cn/
参数列表如下
- client_id:客户端准入标识。
- client_secret:客户端秘钥。
- grant_type:授权类型,填写authorization_code,表示授权码模式
- code:授权码,就是刚刚获取的授权码,注意:授权码只使用一次就无效了,需要重新申请。
- redirect_uri:申请授权码时的跳转url,一定和申请授权码时用的redirect_uri一致。
httpclient脚本如下:
### 授权码模式
### 第一步申请授权码(浏览器请求)/oauth/authorize?client_id=c1&response_type=code&scope=all&redirect_uri=http://www.51xuecheng.cn
### 第二步申请令牌
POST {{auth_host}}/auth/oauth/token?client_id=XcWebApp&client_secret=XcWebApp&grant_type=authorization_code&code=CTvCrB&redirect_uri=http://www.51xuecheng.cn
申请令牌成功如下所示:
{
"access_token": "368b1ee7-a9ee-4e9a-aae6-0fcab243aad2",
"token_type": "bearer",
"refresh_token": "3d56e139-0ee6-4ace-8cbe-1311dfaa991f",
"expires_in": 7199,
"scope": "all"
}
说明:
1、access_token,访问令牌,用于访问资源使用。
2、token_type,bearer是在RFC6750中定义的一种token类型,在携带令牌访问资源时需要在head中加入bearer 空格 令牌内容
3、refresh_token,当令牌快过期时使用刷新令牌可以再次生成令牌。
4、expires_in:过期时间(秒)
5、scope,令牌的权限范围,服务端可以根据令牌的权限范围去对令牌授权。
2)密码模式
密码模式相对授权码模式简单,授权码模式需要借助浏览器供用户亲自授权,密码模式不用借助浏览器,如下图:
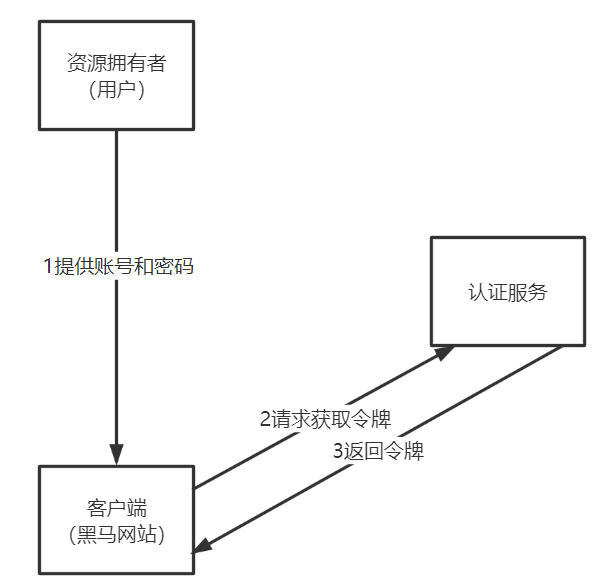
1、资源拥有者提供账号和密码
2、客户端向认证服务申请令牌,请求中携带账号和密码
3、认证服务校验账号和密码正确颁发令牌。
开始测试:
1)POST请求获取令牌
/auth/oauth/token?client_id=XcWebApp&client_secret=XcWebApp&grant_type=password&username=shangsan&password=123
参数列表如下:
- client_id:客户端准入标识。
- client_secret:客户端秘钥。
- grant_type:授权类型,填写password表示密码模式
- username:资源拥有者用户名。
- password:资源拥有者密码。
2)授权服务器将令牌(access_token)发送给client
使用httpclient进行测试
### 密码模式
POST {{auth_host}}/auth/oauth/token?client_id=XcWebApp&client_secret=XcWebApp&grant_type=password&username=zhangsan&password=123
返回示例:
{
"access_token": "368b1ee7-a9ee-4e9a-aae6-0fcab243aad2",
"token_type": "bearer",
"refresh_token": "3d56e139-0ee6-4ace-8cbe-1311dfaa991f",
"expires_in": 6806,
"scope": "all"
}
这种模式十分简单,但是却意味着直接将用户敏感信息泄漏给了client,因此这就说明这种模式只能用于client是我们自己开发的情况下。
3、使用JWT令牌
在认证服务中配置jwt令牌服务,即可实现生成jwt格式的令牌,
@Configuration
public class TokenConfig {
...
@Autowired
TokenStore tokenStore;
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey(SIGNING_KEY);
return converter;
}
@Autowired
private JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter;
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(accessTokenConverter());
}
...
}
拿到了jwt令牌下一步就要携带令牌去访问资源服务中的资源,本项目各个微服务就是资源服务,比如:内容管理服务,客户端申请到jwt令牌,携带jwt去内容管理服务查询课程信息,此时内容管理服务要对jwt进行校验,只有jwt合法才可以继续访问。如下图:
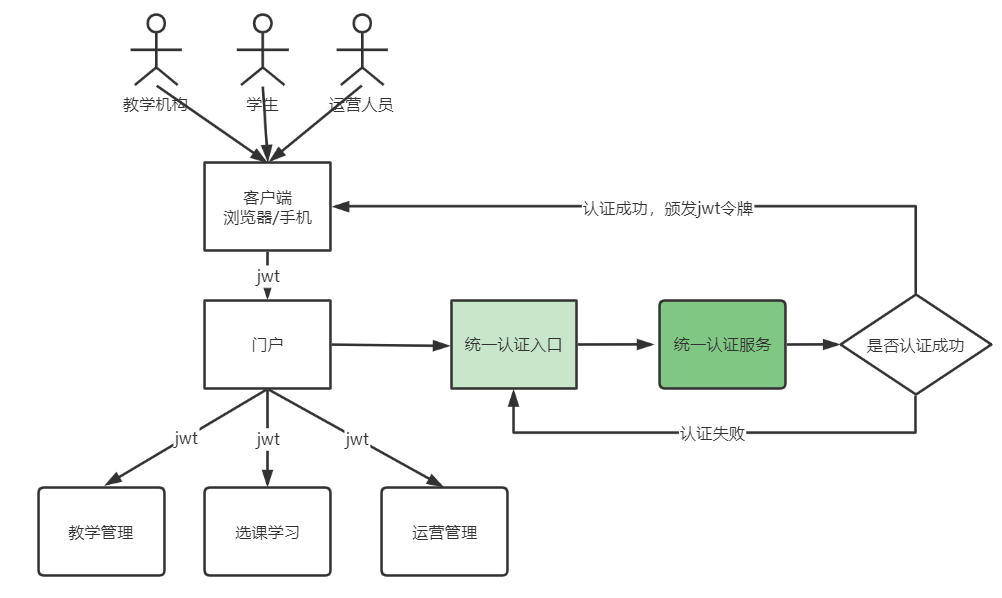
1、在内容管理服务的content-api工程中添加依赖
<!--认证相关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、配置TokenConfig和ResouceServerConfig 到内容管理的api工程的config包下。
@Configuration
public class TokenConfig {
String SIGNING_KEY = "mq123";
@Autowired
@Lazy
private JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter;
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(accessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey(SIGNING_KEY);
return converter;
}
}
可以在ResouceServerConfig类中配置需要认证的url。
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)
public class ResouceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
//资源服务标识
public static final String RESOURCE_ID = "xuecheng-plus";
@Autowired
TokenStore tokenStore;
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID)//资源 id
.tokenStore(tokenStore)
.stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/r/**","/course/**").authenticated()//所有/r/**的请求必须认证通过
.anyRequest().permitAll()
;
}
}
重启内容管理服务
使用httpclient测试:
1、访问根据课程id查询课程接口
### 查询课程信息
GET http://localhost:63040/content/course/2
返回:
{
"error": "unauthorized",
"error_description": "Full authentication is required to access this resource"
}
从返回信息可知当前没有认证。
下边携带JWT令牌访问接口:
1、申请jwt令牌
采用密码模式去认证服务申请令牌。
2、携带jwt令牌访问资源服务地址
### 携带token访问资源服务
GET http://localhost:63040/content/course/2
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhdWQiOlsicmVzMSJdLCJ1c2VyX25hbWUiOiJ6aGFuZ3NhbiIsInNjb3BlIjpbImFsbCJdLCJleHAiOjE2NjQzMzM0OTgsImF1dGhvcml0aWVzIjpbInAxIl0sImp0aSI6IjhhM2M2OTk1LWU1ZGEtNDQ1Yy05ZDAyLTEwNDFlYzk3NTkwOSIsImNsaWVudF9pZCI6ImMxIn0.73eNDxTX5ifttGCjwc7xrd-Sbp_mCfcIerI3lGetZto
在请求头中添加Authorization,内容为Bearer 令牌,Bearer用于通过oauth2.0协议访问资源。
如果携带jwt令牌且jwt正确则正常访问资源服务的内容。如果不正确则报令牌无效的错误:
{
"error": "invalid_token",
"error_description": "Cannot convert access token to JSON"
}
4、获取用户身份
jwt令牌中记录了用户身份信息,当客户端携带jwt访问资源服务,资源服务验签通过后将前两部分的内容还原即可取出用户的身份信息,并将用户身份信息放在了SecurityContextHolder上下文,SecurityContext与当前线程进行绑定,方便获取用户身份。
还以查询课程接口为例,进入查询课程接口的代码中,添加获取用户身份的代码
@ApiOperation("根据课程id查询课程基础信息")
@GetMapping("/course/{courseId}")
public CourseBaseInfoDto getCourseBaseById(@PathVariable("courseId") Long courseId){
//取出当前用户身份
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
System.out.println(principal);
return courseBaseInfoService.getCourseBaseInfo(courseId);
}